Content moderation is a critical process for maintaining the integrity, safety, and usability of online platforms, especially those reliant on user-generated content (UGC). As digital platforms grow and diversify, the need for effective content moderation becomes increasingly vital. Here, in an effort to provide your organization with a complete understanding of this burgeoning online necessity, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of content moderation. From basic concepts to advanced techniques, the following ensures relevance for both newcomers and seasoned professionals.

What is content moderation?
Content moderation refers to the practice of monitoring and managing user-generated content to ensure it complies with legal, ethical, and community standards. This process is crucial for preventing the spread of harmful content, such as hate speech, misinformation, and explicit material, thereby safeguarding the user experience and brand reputation.
The role of content moderation is multifaceted. It guards digital spaces, actively preventing the proliferation of harmful content. This includes a wide range of material, from hate speech and misinformation to explicit content, all of which can significantly impact the user experience. In the absence of effective moderation, online platforms could quickly become hotbeds for negative behavior and harmful information, which not only affects users but can also tarnish the reputation of the platform itself.
Content moderation is not a one-size-fits-all solution
Moreover, content moderation isn't a one-size-fits-all solution; it varies greatly depending on the platform, its audience, and the nature of the content it hosts. What might be acceptable on a professional networking site could be entirely inappropriate on a family-friendly forum. Thus, moderators must be attuned not only to the content itself but to the context in which it appears.
What does a content moderator do?
A content moderator's role involves scrutinizing user submissions, such as images, videos, and text, and deciding whether they adhere to specific guidelines. Moderators may remove, flag, or escalate content based on its nature, context, and impact.
Here are some common moderator tasks broken down into bite-size pieces of information:
Reviewing submissions: Moderators meticulously assess user-generated content, such as text posts, images, and videos, ensuring they adhere to the platform's guidelines.
Enforcing guidelines: They are responsible for enforcing the community and content guidelines set by the platform, which may involve content removal, editing, or flagging.
Handling user reports: Moderators address user reports about inappropriate or harmful content, evaluating each case and taking necessary actions.
Escalating Issues: When encountering sensitive or complex issues, moderators often escalate them to higher authorities or specialized teams within the organization.
Maintaining community standards: They play a key role in upholding the platform's standards, contributing to a safe and respectful online environment.
Feedback and communication: Moderators often provide feedback to users about their content and explain moderation decisions to foster understanding and transparency.
Collaborating with teams: They work closely with other teams, like legal, security, and customer service, to address broader issues related to content and user safety.
Escalating issues: When encountering sensitive or complex issues, moderators often escalate them to higher authorities or specialized teams within the organization.
Collaborating with teams: They work closely with other teams, like legal, security, and customer service, to address broader issues related to content and user safety.
Updating guidelines: Moderators help in revising and updating content guidelines in response to new trends, user behavior, and legal requirements.
High priority content flagged and removed by moderators
While the types of content flagged and removed by moderators is relative to a number of factors, such as community guidelines and national law, there are several types of harmful content that are widely recognized as illegal across most jurisdictions around the world. Here are the top five:
Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM): Any content that sexually exploits children, such as images and videos, is illegal universally. This is one of the most aggressively targeted forms of illegal content online.
Terrorist Violence and Extremist Content (TVEC): Content that promotes terrorist activities, radicalization, or extreme ideologies, especially those inciting violence, is illegal in most countries. This includes recruitment materials, instructions for terrorist acts, and glorification of terrorism.
Hate Speech and Incitement to Violence: While the definition of hate speech can vary by jurisdiction, content that incites hatred or violence against individuals or groups based on race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or other protected characteristics is generally illegal.
Human Trafficking and Exploitation: Content that facilitates or promotes human trafficking, including sexual exploitation and forced labor, is illegal worldwide. This also includes content that advertises or sells humans for exploitation.
Illegal Drug Trafficking and Sale: Online content that involves the sale or promotion of illegal drugs is prohibited in most countries. This includes platforms that facilitate the purchase and distribution of controlled substances.
These categories of content are not only harmful but also universally recognized as illegal, leading to concerted efforts by governments, law enforcement agencies, and online platforms to detect, remove, and prosecute related activities.
Common content moderation guidelines

Ensuring a safe online environment
But content moderation isn't just about censorship or removal of content. It's about creating a safe, inclusive, and respectful online environment. This involves a delicate balancing act between allowing freedom of expression and ensuring that this freedom doesn't infringe on the safety and rights of others. It's about discerning the fine line where free speech ends and harmful content begins.
Oftentimes, an online community’s specified content guidelines will help define this line, but without these guidelines, moderators are forced to rely first on what is legal (in a federal sense) and finally on their own best judgment.
Most platforms have established guidelines outlining what is and isn't acceptable. These guidelines are crucial for moderators to make consistent and fair decisions. These include but aren’t necessarily limited to:
1. Prohibition of hate speech and harassment: Platforms typically ban content that promotes hate or violence against individuals or groups based on race, ethnicity, national origin, gender, religion, or other protected characteristics. This also extends to bullying and harassment, both of which are not tolerated.
2. No explicit or offensive content: To maintain a respectful environment, explicit content, including nudity, pornography, and graphic violence, is often prohibited. This also encompasses content that is broadly offensive or disturbing.
3. Misinformation and fake news: With the rise of digital media, curbing misinformation has become crucial. Many platforms actively remove or flag content that spreads false or misleading information, particularly if it poses a risk to public safety or health.
4. Intellectual property rights: Respecting copyrights and trademarks is a fundamental aspect of content guidelines. Unauthorized use of copyrighted materials, pirated content, or counterfeit goods is generally not allowed.
5. Privacy and personal information: Protecting user privacy is key. Sharing personal or sensitive information about others without consent is usually prohibited to prevent doxing and other privacy breaches.
6. Spam and malicious content: Guidelines often include a ban on spam, which can range from unsolicited advertising to phishing attempts and other forms of malicious digital content.
7. User engagement and authenticity: Encouraging genuine interactions, many platforms discourage inauthentic behaviors like fake accounts, artificially boosting content engagement, or other manipulative practices.
8. Compliance with local laws: Content must often comply with the legal requirements of the country in which the platform operates. This includes laws related to hate speech, defamation, and other local regulations.
9. Reporting and enforcement mechanisms: Effective guidelines also include clear procedures for users to report violations and for moderators to take appropriate action, which may range from content removal to user bans.
Common content moderation tools

Various tools and software, like the hash matching and database technologies offered by Videntifier, play a huge role in content moderation. These tools range from AI-driven systems, to manual review interfaces, to hash matching technology, each serve different aspects of the moderation process. Each type of tool caters to specific needs in the content moderation process, ensuring a comprehensive approach to maintaining online safety and integrity.
AI-driven systems
AI tools use advanced algorithms to automate large parts of the moderation process. Key capabilities include:
Automated Content Filtering: Identifying and flagging content that violates preset guidelines.
Pattern Recognition: Evolving to recognize complex content patterns through machine learning.
Sentiment Analysis: Evaluating textual content to gauge tone and identify negative interactions.
Manual review interfaces
These are vital for the nuanced decision-making that AI cannot fully replicate. Features include:
User-Friendly Dashboards: Organized interfaces for moderators to review and manage content.
Contextual Information: Providing background information to aid in decision-making.
Collaboration Features: Allowing teams to work together on complex moderation tasks.
Hash matching technology
A crucial addition to the toolkit, hash matching offers a sophisticated method for content identification. It involves:
Digital Fingerprinting: Creating unique digital "hashes" of known harmful content. These hashes are like fingerprints, identifying specific files.
Rapid Identification: Comparing hashes of new content with a database of these fingerprints to quickly identify and flag previously flagged content.
Efficiency and Accuracy: Hash matching is especially effective for quickly scanning large volumes of content while maintaining high accuracy.
This method of moderation allows for a multitude of image/video matching capabilities, especially when moderating against images that have been modified to avoid detection, as illustrated in the chart below. As you scroll, consider how each of these match types might serve various moderation use cases:

The integration of AI systems, manual review platforms, and hash matching technology creates a robust content moderation framework. AI offers scalability and speed, manual reviews bring contextual understanding and nuanced judgment, and hash matching provides a fast, accurate method for identifying known harmful content. Together, these tools form a multi-layered defense against inappropriate or harmful online material, crucial for the health and safety of digital communities.
Using automated tools to support moderators’ mental health

In recent years, the mental health crisis among content moderators has become a pressing issue. Moderators are often exposed to disturbing and violent content— sometimes of an illegal nature, though not always, as this type of content may be legal in certain locales—which can take a significant toll on their mental well-being. In this context, content moderation tools play a crucial role in mitigating these challenges and protecting the mental health of moderators.
1. Automated filtering
Advanced content moderation tools, can significantly reduce the exposure of human moderators to potentially traumatic content. By automatically filtering out explicit and harmful material before it reaches human eyes, these tools act as a first line of defense. This not only streamlines the moderation process but also lessens the psychological burden on human moderators.
2. Prioritization and workflow management
Content moderation tools can categorize and prioritize content, ensuring that human moderators deal with less severe cases first, gradually moving to more sensitive content. This managed approach can help in reducing the sudden impact of disturbing content, providing a more controlled work environment.
3. Mental health support features
Some content moderation tools are being designed with built-in support features for moderators. These may include options for moderators to take immediate breaks, access to mental health resources directly through the platform, and tools to anonymously report distress. Some moderation tools, such as those provided by Videntifier, include built-in blur effects to ensure moderators are not exposed to more harmful content than is necessary. See below:
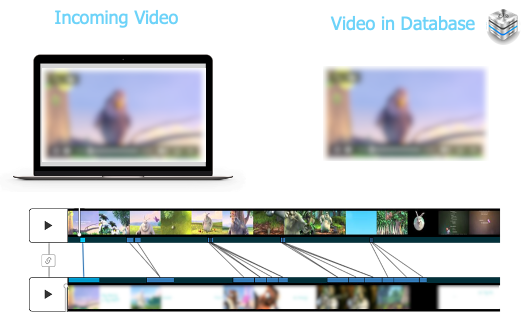
4. Training and preparedness
Tools can also provide training modules for moderators, preparing them for the nature of the content they might encounter. This training can include coping mechanisms, awareness about mental health issues, and strategies to manage stress and trauma.
5. Reducing isolation
Collaboration features within moderation tools can help reduce the sense of isolation that moderators may feel. By enabling moderators to work as a team, share experiences, and support each other, these tools foster a community approach to moderation.
UGC content moderation

Navigating the challenges of UGC content moderation
User-generated content (UGC) is the backbone of many online platforms. In essence, UGC makes up the vibrant, diverse voices of a platform’s user base. But with this creativity comes one of the biggest challenges of moderation: UGC content moderation is a delicate balance between fostering a free, creative exchange of ideas and maintaining a safe, respectful online environment.
The core of effective UGC moderation lies in understanding the context. What might be acceptable in one forum could be offensive or harmful in another. Moderators must be adept at interpreting not just the content but its intended meaning, audience, and potential impact. This demands a nuanced approach, where the understanding of cultural and contextual subtleties becomes as crucial as the enforcement of rules.
Another aspect of UGC moderation is the volume. The sheer quantity of content generated every minute presents a logistical challenge. Here, technology plays a crucial role. AI-driven tools and hash matching technologies can help manage the flow, flagging potential issues for human review. But as things currently stand, the human element remains indispensable. Automated systems can identify explicit content or hate speech, but they may struggle with subtleties like sarcasm or cultural references. Therefore, a combined approach using both AI and human judgment often yields the best results.
Finally, transparency and communication are key. Platforms need to clearly communicate their content guidelines to users, creating an environment where expectations are understood. Equally important is the feedback loop - when users understand why their content was moderated, it fosters a sense of fairness and respect.
Why is content moderation important for user-generated campaigns?
Moderation in user-generated campaigns ensures that the content aligns with brand values and community standards, thus enhancing campaign effectiveness and protecting brand reputation. User-generated campaigns, leveraging content created by users rather than brands themselves, have become a popular and effective marketing strategy. However, their success hinges significantly on content moderation. Why is this process so crucial for these campaigns?
Brand safety
User-generated content (UGC) is unpredictable. Without proper oversight, a brand risks associating itself with inappropriate or offensive material. Moderation filters out such content, aligning the campaign with the brand's values and public image.
Trust
When users see a brand taking responsibility for the content it showcases, especially in user-generated campaigns, it builds trust. Consumers are more likely to engage with and contribute to campaigns where they feel safe and respected.
User experience
Well-moderated campaigns are free from spam, irrelevant or harmful content, making the user experience more enjoyable and engaging. This not only attracts more participation but also fosters a positive community around the brand.
Legal compliance
User-generated content can sometimes inadvertently violate copyright or privacy laws. Through diligent moderation, brands can avoid legal pitfalls and maintain ethical standards.
Content moderation for trust and safety teams

How the corporate sphere handles content moderation
In the corporate sphere, content moderation is handled by specialized trust and safety teams. These teams focus on establishing clear content policies and rely on a blend of advanced technology and human oversight for moderation. They use AI and machine learning tools to efficiently filter large volumes of content, complemented by human moderators who address complex or sensitive issues.
Corporations also invest in continuous training and support for their moderation teams, focusing on mental health and resilience. Additionally, they often collaborate with external experts and law enforcement for broader insights and crisis management. Transparency in moderation efforts and active user engagement are key to building trust and maintaining a safe online environment. This holistic approach ensures that corporate platforms remain safe, respectful, and compliant with legal standards.

Comments